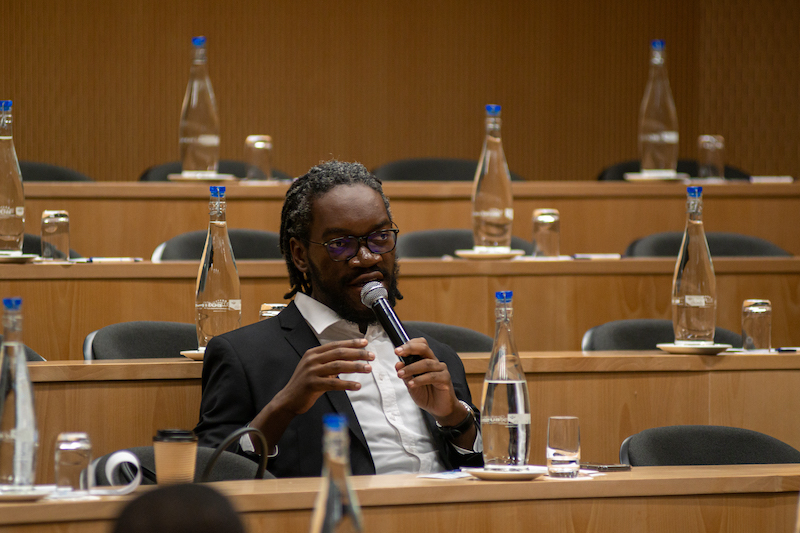
Last month I had the opportunity to attend and speak at the premier event of the XRPL Ledger (XRPL) community – The Apex Developer Summit in Las Vegas, USA. At the event, which is hosted annually by Ripple and the XRPL Foundation I got to meet and engage with the XRPL community, which included David Schwartz, a co-founder and current CTO at Ripple.
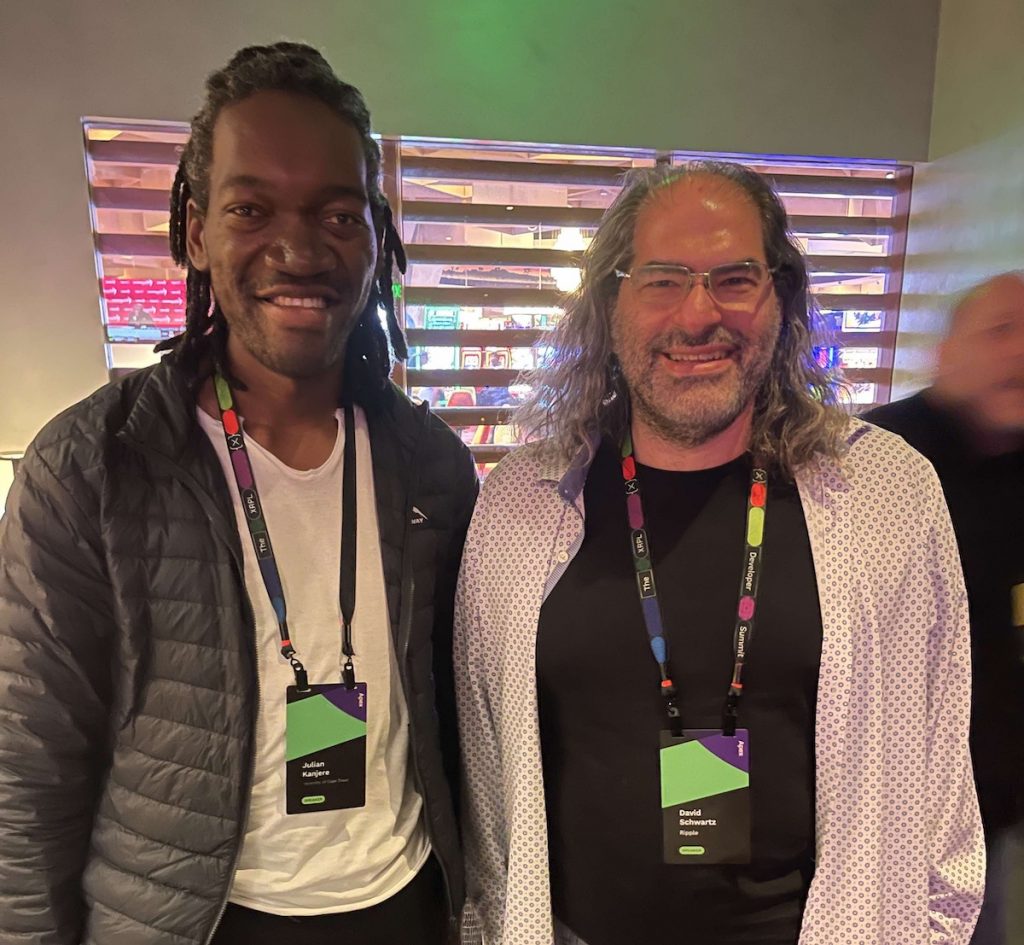

Before jumping into a summary of David Schwartz talk on The next iteration of XRPL, recall that XRPL is a decentralised, public blockchain led by a global developer community – think of XRPL as a public good. XRPL makes use of a federated byzantine agreement algorithm that enables fast & cheap transactions with finality achieved in 3 to 5 seconds (in simpler terms, transactions with XRP or XRPL-issued assets complete in 3 – 5 seconds). You can learn more about the XRPL here and join the community on discord here.
Now, back to David Schwartz’s keynote, he started the talk with a look at the XRPL design fundamentals which include:
- An integrated decentralised exchange (DEX) – the XRPL has features an inbuilt DEX since the beginning (circa 2012).
- Invariant checking – the ledger has an ability to check for bugs without corrupting the ledger.
- Rekeyable accounts – XRPL features rekeyable accounts, which is a feature that allows for changing the transaction signing key without changing receiving key.
- Issued assets – XRPL supports the ability to issue custom assets (e.g. stablecoins or anything fungible that has value and behaves like currency) with ease.
David went on to note some of the exciting XRPL innovations which include:
- XLS-20d – a proposed standard to issue NFTs on the XRPL i.e. mint/burn/hold/trade NFTs. The XLS-20d is designed for scale.
- Project Clio – a development initiative to create massive storage reduction for servers that handle queries from clients. This will increase throughput, reduce cost to access the ledger and allow the ledger to scale (bearing in mind that the ledger cannot go any faster than consensus can).
- Hooks -a feature of XRPL that allows developers to add smart-contract like functionality to the XRPL. Hooks are small, efficient pieces of code being defined on an XRPL account, allowing logic to be executed before and/or after XRPL transactions.
- Sidechains – a feature of XRPL that allows anyone to run a sidechain to the XRP Ledger while having the freedom to decide how their chains work. You want XRPL mechanics but assets from other chains e.g. running an EVM sidechain to allow even more developers easy access to XRPL’s feature set and bring existing Solidity-based smart contracts written for EVM-compatible chains to the XRPL. Sidechains allow you to innovate at the blockchain level i.e. L1 level e.g. if you wish to tweak the TPS you can do so. Sidechains ultimately provide horizontal scalability.
In addition to David’s keynote, the summit included other keynotes on NFTs, blockchain and law, and new ways to build with some of the ecosystem tools. Here are links to the keynotes:
- The State of the XRP Ledger Foundation, Thomas Silkjaer & Scott Branson
- The Future of Identity Tokenization, Julian Vergel de Dios
- New Ways to Build on Xumm, Wietse Wind
- Blockchain: Law as an Enabler and a Stumbling Block, N.S. Nappinai
- The Intersection of Art and Technology, David Schwartz & Ragzy X
And then I earlier I mentioned that I got to speak at the conference. I gave a talk on how to send and receive XRPL-based assets in low-tech environments e.g. in place where there is no internet connectivity or smartphones. Here is the link to my talk – Transacting in Low-Tech Environments, Julian Kanjere – I will write a post on this soon.




 Outside of the Algorand events, I got to network with some of the TOKEN2049 crowd, enjoy the views from the top of the Marina Bay Sands and capped of the weekend with the F1 Marina Bay Night Race which did not disappoint.
Outside of the Algorand events, I got to network with some of the TOKEN2049 crowd, enjoy the views from the top of the Marina Bay Sands and capped of the weekend with the F1 Marina Bay Night Race which did not disappoint.
 The FoodPrint team is growing, and in particular, our tech team is firing on all cylinders. We have an immediate need for a Community Manager – someone with expertise in agriculture, connections to farmers and cooperatives, entrepreneurship and community building. In addition, we are also seeking to partner with more AgriHubs/food cooperatives and bulk produce buyers/retailers – we would like them to hop on board as early adopters of our platform. If you can assist with either, drop us an email
The FoodPrint team is growing, and in particular, our tech team is firing on all cylinders. We have an immediate need for a Community Manager – someone with expertise in agriculture, connections to farmers and cooperatives, entrepreneurship and community building. In addition, we are also seeking to partner with more AgriHubs/food cooperatives and bulk produce buyers/retailers – we would like them to hop on board as early adopters of our platform. If you can assist with either, drop us an email 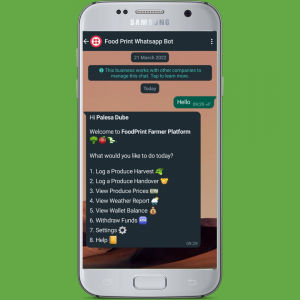 At the end of 2021, we started work on our WhatsApp chatbot, and I am excited to say that we are almost ready to pilot this. Using our low-tech WhatsApp chatbot, farmers can register to the FoodPrint platform, and everytime they harvest and sell produce, they record this on the chatbot – creating a digital record (anchored on the blockchain) that links them to potential buyers and finance service providers (in future). The WhatsApp chatbot will be free
At the end of 2021, we started work on our WhatsApp chatbot, and I am excited to say that we are almost ready to pilot this. Using our low-tech WhatsApp chatbot, farmers can register to the FoodPrint platform, and everytime they harvest and sell produce, they record this on the chatbot – creating a digital record (anchored on the blockchain) that links them to potential buyers and finance service providers (in future). The WhatsApp chatbot will be free The FoodPrint platform also supports product-specific QR Codes for consumers to scan, and read the claims or the story behind the food they are buying or about to consume. Here is an example – scan with your mobile device – and see what a provenance record looks like.
The FoodPrint platform also supports product-specific QR Codes for consumers to scan, and read the claims or the story behind the food they are buying or about to consume. Here is an example – scan with your mobile device – and see what a provenance record looks like. We have partnered with PEDI AgriHub in Philippi Cape Town, and are piloting a fresh produce harvest box in the Southern Suburbs of Cape Town! We are especially excited about this as this is an immediate way for us to add value to local farmers and provide the farmers they support with market access. The harvest box contains fresh, quality seasonal produce. If you would like to purchase a weekly fresh produce box, you can get in touch
We have partnered with PEDI AgriHub in Philippi Cape Town, and are piloting a fresh produce harvest box in the Southern Suburbs of Cape Town! We are especially excited about this as this is an immediate way for us to add value to local farmers and provide the farmers they support with market access. The harvest box contains fresh, quality seasonal produce. If you would like to purchase a weekly fresh produce box, you can get in touch  And lastly, last month, I had the opportunity to share how FoodPrint is bringing blockchain technology to food supply chains in sub-Saharan Africa at a blockchain workshop in Zurich, arranged by the
And lastly, last month, I had the opportunity to share how FoodPrint is bringing blockchain technology to food supply chains in sub-Saharan Africa at a blockchain workshop in Zurich, arranged by the